Solar power supply is revolutionizing the way we generate electricity, providing a clean, renewable, and sustainable energy solution. In this article, we will explore the benefits of solar power, the technology behind it, and its potential to transform our energy landscape.
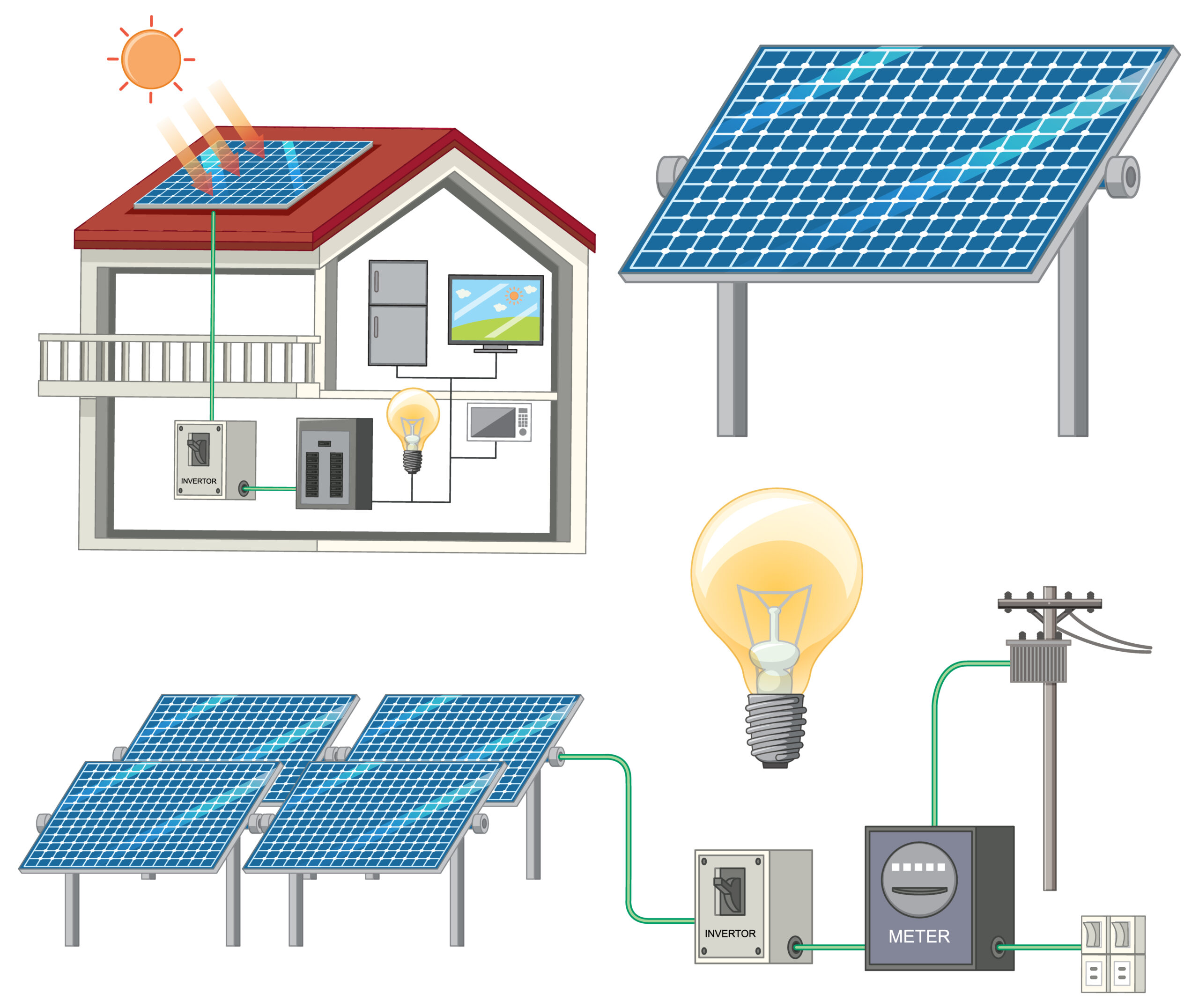
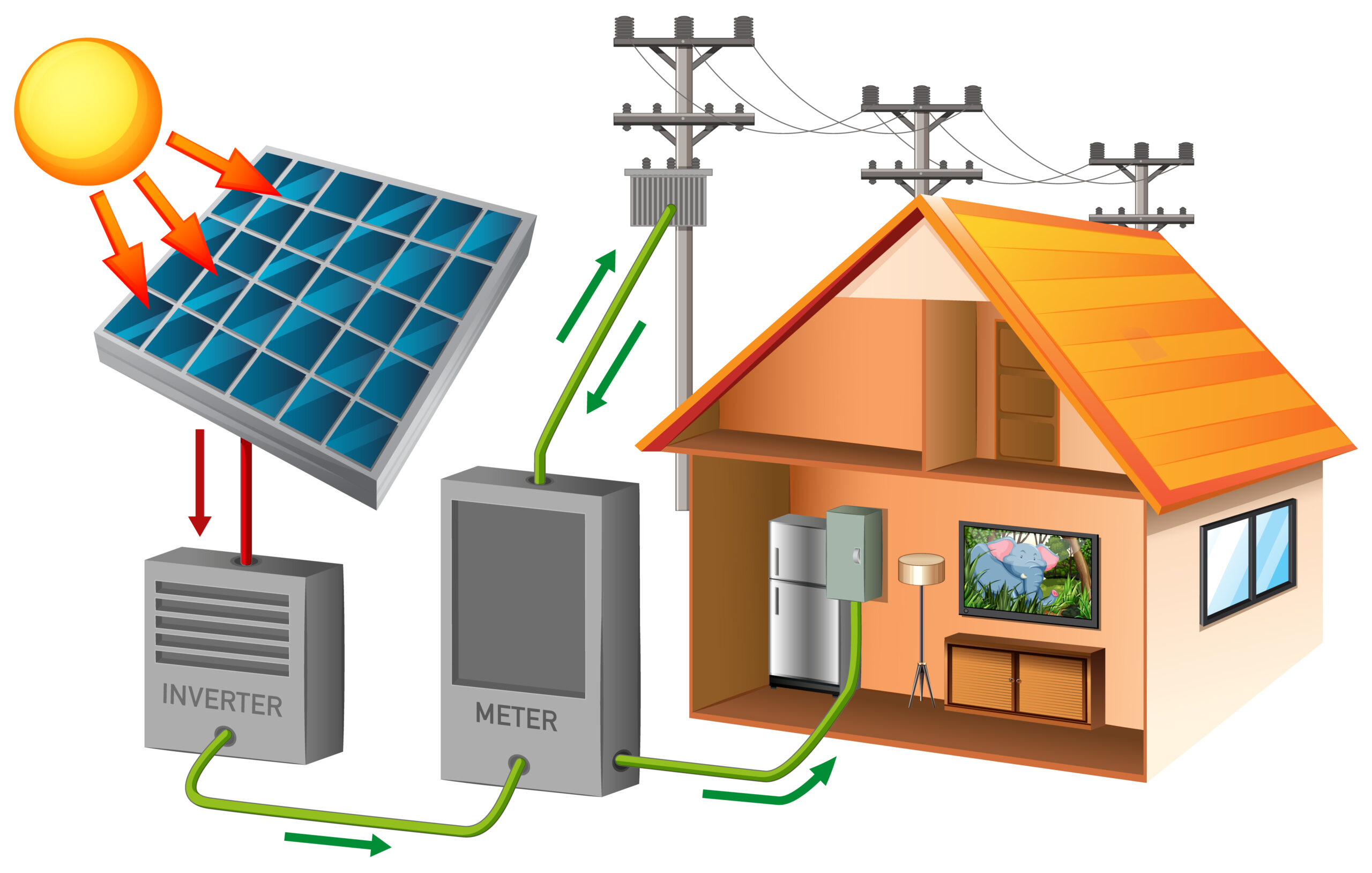
- Understanding Solar Power: Solar power supply is the conversion of sunlight into usable electricity through photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells, typically made of silicon, absorb sunlight and generate a direct current (DC) electrical charge. This DC power is then converted into alternating current (AC) using inverters, making it compatible with standard electrical systems.
- The Advantages of Solar Power: Solar power offers numerous advantages over traditional energy sources:
a. Renewable and Sustainable: Solar energy is derived from the sun, an inexhaustible resource, making it a sustainable solution that can be harnessed for generations to come.
b. Environmental Benefits: Solar power produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants during operation, reducing carbon footprints and combating climate change.
c. Cost Savings: Once installed, solar power systems can generate free electricity, leading to significant savings on utility bills. Additionally, some countries offer incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, to promote solar energy adoption.
d. Energy Independence: Solar power allows individuals and businesses to generate their own electricity, reducing reliance on the grid and providing energy security, particularly in remote or off-grid locations.
Components of a Solar Power System:
a. Solar Panels: These panels, also known as PV modules, consist of interconnected solar cells that absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity.
b. Inverters: Inverters convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity for use in homes and businesses.
c. Mounting and Racking: Solar panels need to be securely mounted and positioned to maximize exposure to sunlight. Mounting and racking systems ensure proper installation and orientation.
d. Batteries (for Off-grid Systems): In off-grid solar systems, batteries store excess electricity generated during the day for use during nighttime or when sunlight is limited.
e. Monitoring Systems: Monitoring systems track the performance of solar panels, enabling users to assess energy production and identify any issues.
Applications of Solar Power: Solar power can be used in various applications:
a. Residential: Many homeowners install solar panels on their rooftops to generate clean electricity for their homes, reducing reliance on the grid and saving money.
b. Commercial: Businesses are increasingly embracing solar power to meet their energy needs, lower operating costs, and demonstrate environmental stewardship.
c. Utility-Scale: Large-scale solar power plants generate electricity on a massive scale, supplying power to communities and contributing to the overall energy mix.
d. Off-grid and Remote Areas: Solar power provides a viable solution for powering off-grid and remote locations, where accessing the traditional power grid is challenging.
Overcoming Challenges and Future Outlook
While Solar power supply has seen significant growth, several challenges remain, including initial installation costs, intermittent power generation, and the need for storage solutions. However, advancements in technology, declining costs, and increased efficiency are overcoming these obstacles. Innovations like solar batteries and smart grid integration are enhancing the reliability and usability of solar power.
Solar Power and the Environment:
Solar power plays a crucial role in mitigating the environmental impact of traditional energy sources. By shifting to solar power, we can reduce reliance on fossil fuels, decrease air pollution, and combat climate change. Solar energy produces no greenhouse gas emissions, particulate matter, or harmful pollutants during operation. It helps preserve natural resources and ecosystems by minimizing water usage compared to conventional power generation methods. By embracing solar power, we can contribute to a cleaner and healthier planet for future generations.
The Economic Benefits of Solar Power:
Solar power not only benefits the environment but also stimulates economic growth. The solar industry creates job opportunities across various sectors, from manufacturing and installation to research and development. As solar technology becomes more affordable and accessible, it fosters local economic development and promotes energy independence. Additionally, the savings on electricity bills resulting from solar power installations provide financial relief for homeowners, businesses, and communities. The shift towards solar power reduces dependence on imported energy sources, increasing energy security and stability. Overall, solar power offers a positive economic outlook by driving innovation, job creation, and cost savings in the long run.
Advancements in Solar Technology:
The field of solar technology is constantly evolving, with ongoing advancements and innovations enhancing the efficiency, affordability, and aesthetics of solar power systems. Some notable advancements include:
a. Increased Efficiency: Researchers are continuously improving solar cell designs and materials to enhance energy conversion efficiency, allowing for higher power generation from limited space.
b. Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): BIPV integrates solar panels seamlessly into building materials like roofs, windows, and facades, providing aesthetic appeal while generating electricity.
c. Thin-Film Solar Cells: Thin-film solar cells offer flexibility and versatility, allowing for applications in curved surfaces, portable devices, and building-integrated solutions.
d. Energy Storage Solutions: Battery storage systems are becoming more efficient and affordable, enabling solar energy to be stored for use during cloudy periods or at night, enhancing the reliability of solar power.
Government Initiatives and Support:
Governments worldwide are recognizing the potential of solar power and implementing supportive policies and incentives. Many countries offer feed-in tariffs, net metering programs, tax credits, and grants to encourage the adoption of solar energy. These initiatives make solar power more financially viable and attractive to individuals and businesses. Government support also extends to research and development funding, fostering technological advancements in the solar industry. Collaborative efforts between public and private sectors are driving innovation and accelerating the transition to a renewable energy future.
Conclusion:
Solar power supply is a sustainable and environmentally friendly energy solution with significant economic benefits. As technology continues to advance and governments provide support, solar power is poised to play a vital role in our energy landscape. Embracing solar power is not only a step towards energy independence but also a commitment to a greener and more sustainable future. Solar power supply offers a clean, renewable, and sustainable energy solution with numerous advantages. As technology improves and costs decline, solar power is becoming an increasingly viable and accessible option for individuals, businesses, and communities, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future.
